_htm_cmp_pstmdrn110_bnr.gif)
Patients may hear their physician use a variety of unfamiliar terms to describe body positions or motions. This page is presented to describe some of the basic terms that may be used.
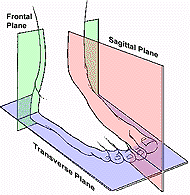
Cardinal Planes
Frontal Plane describes the plane dividing
the front of the body and the back of the body. This plane is pictured
below in green.
Sagittal Plane describes the plane
dividing the left hand and right hand portions of the body. This plane is
pictured below in pink.
Transverse Plane describes the plane
dividing the top portion and bottom portion of the body. This plane is
pictured below in purple.
Directions
Medial describes the location of
something closer to the midline of the body. For example, the big toe is
medial to the little toe.
Lateral describes the location of
something further from the midline of the body. For example, the little
toe is lateral to the big toe.
Dorsal means the top of the foot.
Plantar means the bottom of the foot--the
sole.
Anterior means the front of the
body. For example, your shin bone is anterior to your Achilles
Tendon.
Posterior means the back of the
body. For example, your heel bone lies posterior to your
toes.
Superficial means closer to the skin--less
deep.
Deep, the opposite of superficial, means
further into the body.
Motions
Adduction describes
the motion of bringing something towards the midline of the body. For
example, if the big toe were oriented so it was pointing away from the second
toe and towards the opposite foot, it would be adducted.
Abduction describes the motion of taking
something away from the midline of the body. For example, if the big
little toe were oriented so it was pointing away from the other toes, it would
be abducted.
Dorsiflexion describes
the motion of the foot where the toes or ball of the foot are lifted off the
ground. (See illustration below.)
Plantarflexion describes the motion of the
foot where the toes or ball of the foot is pushed down towards the ground.
(See illustration below.)
Inversion describes the motion of the foot
where the foot is rolling over towards the medial, or inside portion, of the
foot. (See illustration below.)
Eversion describes the motion of the foot
where the foot is rolling over towards the lateral, or outside portion, of the
foot. (See illustration below.)

Pronation is a complicated motion
involving all three cardinal planes. Pronation involves movement of the
arch in a plantarflexed, adducted and everted position.
Supination is the opposite of
pronation. Supination involves movement of the arch in a dorsiflexed,
abducted and inverted position.
Positions
Varus describes
the position of the foot when it is inverted.
Valgus describes the position of the foot
when it is everted.
Cavus
describes a high-arched structural position of the foot (commonly associated
with a supinated foot, described above.
Planus describes
a low-arched structural position of the foot, (commonly associated with a
pronated foot, described above.